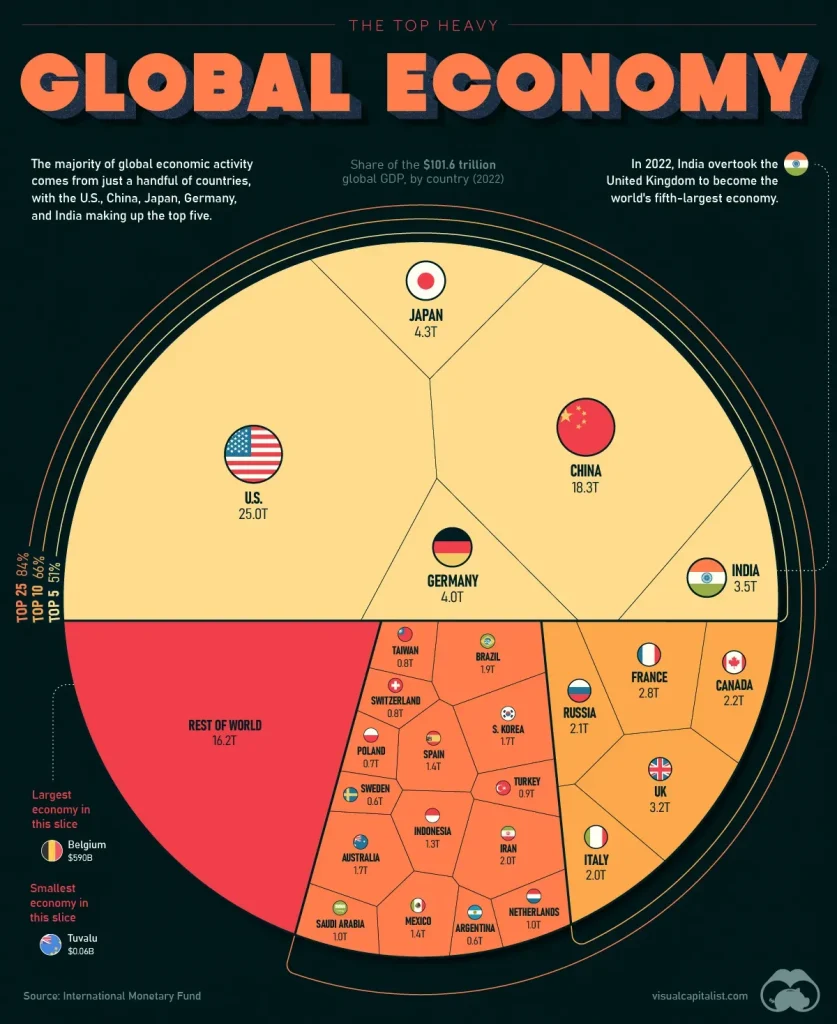
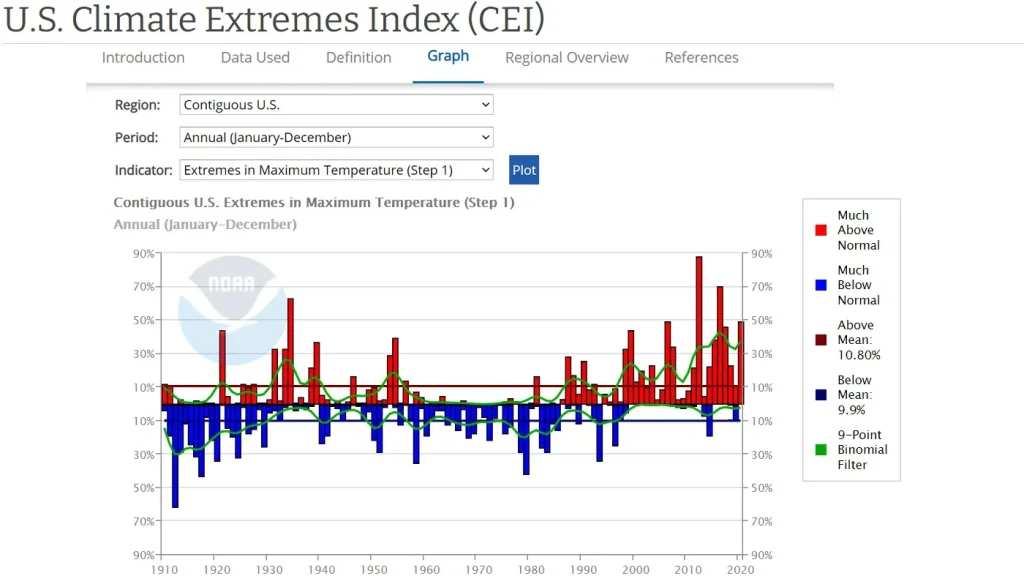
Global News Economy sits at the center of our highly interconnected world, shaping decisions from households budgeting weekly expenses to policymakers drafting long-term strategies for growth and resilience. From the pulse of global markets and fluctuations in exchange rates to the flow of international trade, the landscape translates complex data into a narrative about how economies expand, pause, or reallocate resources. Understanding this landscape means watching core economic trends, central-bank signals, and the way policy shifts intersect with consumer behavior, business investment, and labor markets across regions. In this introductory overview, market analysis serves as a lens to evaluate risk, opportunity, and the timing of capital allocation, linking headline volatility to longer-run trajectories for growth. The discussion culminates by tying policy choices, energy transitions, and technological innovation to the broader global economy, helping readers anticipate how the next quarters may unfold and guiding businesses, investors, and policymakers to align their efforts.
A broader view frames this topic as the global financial landscape, where markets, trade, and policy interact to influence prosperity across nations. The worldwide market environment responds to monetary signals, trade agreements, and technological shifts, creating a dynamic backdrop for investors and policymakers. This alternative framing highlights how cross-border capital flows, supply-chain resilience, and productivity gains shape living standards over time. As such, readers can relate to macro conditions like growth momentum, price stability, and investment climates without relying on the jargon of a single banner term. In short, the narrative remains the same: interconnected economies, evolving trade links, and evolving trends that guide decisions from boardrooms to households.
Global News Economy: A Lens on Global Markets and Market Analysis
The Global News Economy serves as a lens through which we interpret global markets, where equity indices, bond yields, and currency movements respond to policy cues and macro data. Market analysis here goes beyond daily price swings to reveal how investors price in risk, growth, and policy normalization across major economies. By tracing these signals, readers can gauge how the global markets may shift capital toward sectors with stronger growth and healthier liquidity.
In this framework, inflation dynamics and rate expectations shape asset pricing and capital allocation. Descriptive market analysis shows that even as one region cools, persistent price pressures elsewhere can sustain volatility, guiding decisions about diversification and risk management. The Global News Economy thus connects inflation trends, currency cycles, and commodity prices into a coherent picture of the global economy’s current pulse.
International Trade’s Role in the Global News Economy
International trade acts as the bloodstream of the Global News Economy, linking distant producers to global consumers and distributing knowledge across borders. This interconnected web is shaped by tariffs, trade agreements, and the resilience of supply chains to shocks, which together influence pricing, production decisions, and employment across economies. Understanding trade flows helps explain why certain sectors outperform even when domestic indicators are mixed.
Trade dynamics also hinge on trade finance and liquidity, with banks and fintechs enabling smoother cross-border payments that support growth. As regional supply chains diversify—toward regional manufacturing clusters or nearshoring—business models adapt, affecting global markets and the trajectory of the global economy. The interplay between international trade policy and real-world outcomes remains a central driver of investment and policy decisions.
Economic Trends Shaping the Global Economy and Investment Strategy
Economic trends provide the longer-term context for asset prices and policy choices. Growth dispersion across regions, inflation trajectories, and productivity progress form the backbone of investment strategies and government budgets. By tracking GDP growth, unemployment, and consumer confidence, analysts identify where the global economy is gathering momentum and where headwinds may emerge.
Fiscal policy and public investment—whether in infrastructure, education, or research—can amplify or dampen growth in the coming quarters. When combined with advancements in technology and human capital, these fiscal dynamics influence productivity, the allocation of capital, and the sustainability of expansion. Market analysis benefits from synthesizing these macro trends with sector-specific signals to anticipate durable changes in the global economy.
Policy Moves and Central Banks in Global Markets: A Market Analysis
Policy moves, especially from major central banks, have outsized effects on global markets. Interest rate paths, quantitative easing adjustments, and guidance on inflation trajectories steer currency values and bond yields, shaping risk appetite and cross-border investment. In the Global News Economy, market analysis interprets these signals to forecast how financing costs will influence corporate investment and consumer spending.
As inflation cools or accelerates in pockets of the world, policy normalization can proceed at different speeds, affecting relative currency strength and the competitiveness of trade. Investors watch for policy surprises and gradual shifts, translating them into expectations about economic momentum, sector leadership, and the cost of capital across the global economy.
Regional Perspectives: United States, European Union, and Asia in the Global News Economy
Regional perspectives illuminate how diverse growth drivers shape the Global News Economy. In the United States, a robust services sector and consumer demand interact with inflation and rate expectations to influence market psychology and investment flows. Meanwhile, the European Union faces energy security, policy coordination, and structural reforms that affect trade, markets, and regional growth dynamics.
In Asia, manufacturing strength and domestic demand balance global supply chains, with China playing a central role in global markets. This regional mosaic sets the pace for sectoral shifts in technology, renewables, and traditional industries, and underscores how global economy trajectories depend on cross-border collaboration, investment, and policy alignment.
Supply Chain Resilience, Trade Finance, and the Global Economy
Supply chains increasingly emphasize resilience through diversification, nearshoring, and smarter inventory management. This trend interacts with global markets by altering production timing, input costs, and margin dynamics, even as policy signals can shift risk premiums. The focus on supply chain resilience helps explain key movements in the global economy and provides a practical lens for market analysis.
Trade finance and cross-border payments remain essential to sustaining trade flows in uncertain times. Fintech innovations and bank financing solutions improve liquidity, enabling firms to weather disruptions and invest in productivity-enhancing capabilities. As these financial flows strengthen, they support broader growth in the global economy and reaffirm the interconnected nature of markets, trade, and macroeconomic trends.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Global News Economy and why does it matter to investors and policymakers?
The Global News Economy is the integrated system of global markets, international trade, and economic trends that shapes asset prices, policy decisions, and real-world outcomes. Market analysis helps decode how these moving parts interact, guiding investment strategies and policy discussions within the Global News Economy.
How do global markets influence international trade and the global economy?
Global markets—the prices of equities, bonds, currencies, and commodities—affect exchange rates, financing costs, and risk sentiment, which in turn shape international trade flows and the overall global economy. Through careful market analysis, stakeholders assess how policy shifts and capital movements will impact trade costs and supply chains.
What economic indicators are most telling in the Global News Economy?
Key indicators include GDP growth, inflation, unemployment, productivity, and consumer confidence, all interpreted within the Global News Economy. Market analysis combines these signals to identify trends, regional dispersion, and potential inflection points for growth.
How do policy moves by major economies affect market analysis and investment?
Central banks and governments influence interest rates, currency stability, and trade policy, which reshape the global economy and financial markets. Market analysis translates policy signals into expectations for inflation, asset prices, and trade flows.
Why is diversification important in the Global News Economy?
Diversification helps manage cross-border risks exposed to global markets and trade tensions. In the Global News Economy, broad exposure across geographies and sectors, plus resilient supply chains, supports steadier performance as market analysis highlights evolving risk premiums.
What steps can households and businesses take to navigate current economic trends and trade dynamics?
Stay informed with market analysis, monitor policy signals, and adjust pricing, hedges, and supplier networks accordingly. In the Global News Economy, proactive planning—such as supply-chain diversification and currency risk management—helps mitigate shocks and seize opportunities.
| Aspect | Key Points | Implications / Takeaways |
|---|---|---|
| Global Markets Landscape |
|
|
| Trade, Supply Chains, and International Trade Dynamics |
|
|
| Economic Trends and the Outlook |
|
|
| Regional Perspectives and Sectoral Shifts |
|
|
| Market Analysis and Investment Implications |
|
|
Summary
This HTML table distills the core themes from the Global News Economy content into a structured, English-language overview with actionable takeaways for investors, policymakers, and readers seeking a concise understanding of markets, trade, and economic trends.