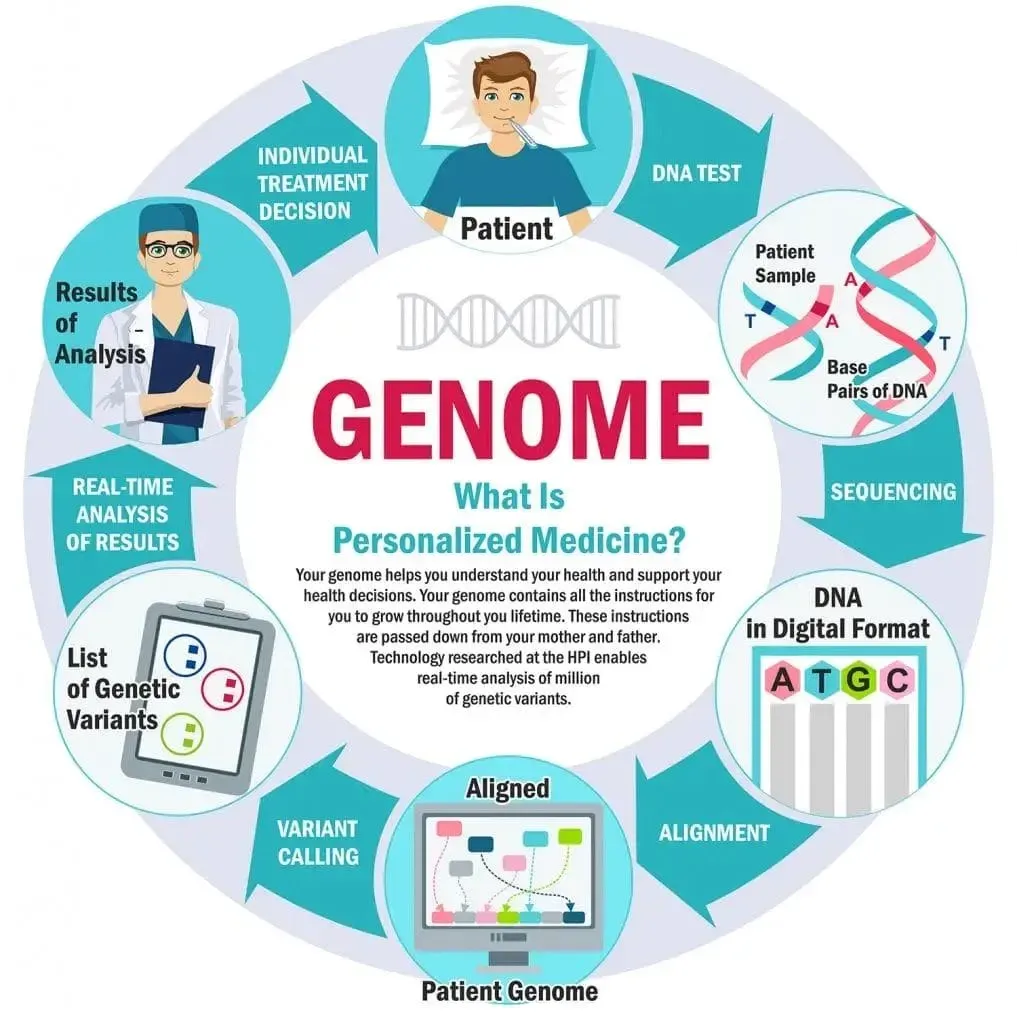
Genetics and Personalized Medicine are redefining health care by turning vast genetic data into tailored strategies that fit each patient’s unique biology, lifestyle, and health history, enabling clinicians to move beyond traditional one-size-fits-all approaches toward care that is proactive, precise, and deeply person-centered. Across research laboratories and clinical settings, scientists and physicians are translating complex genomic information into practical decisions—selecting therapies, predicting risks, guiding prevention, and monitoring response—so care can be faster, safer, more effective, and better aligned with patient preferences and values. These genetics breakthroughs and personalized medicine advances are accelerating as the cost of sequencing falls, data analytics grow more powerful, AI-driven interpretation expands, and interoperability with electronic health records and real-world data becomes routine, turning once-theoretical concepts into everyday medical practice. Genomic research underpins diagnostic accuracy, risk stratification, and targeted therapies, while health tech innovations streamline testing pipelines, empower patients with clearer information, and equip clinicians with real-time decision support that improves outcomes and reduces unnecessary interventions. This introductory overview explains why Genetics and Personalized Medicine matter now, what it means for everyday health decisions, and what we can reasonably anticipate in the near term as science, policy, and technology converge.
A genome-informed approach to care reshapes how we think about disease risk, diagnosis, and treatment, moving beyond generic guidelines toward interventions that reflect an individual’s biology. What’s more, patient-specific therapies are becoming feasible as our understanding of genes, protein networks, and metabolism informs targeted strategies. In this evolving landscape, precision health relies on multi-omics data and real-world evidence to tailor prevention and therapy to people rather than populations. Clinicians are drawing on genome-focused diagnostics, pharmacogenomics, and data-driven decision tools to guide choices that maximize benefit and minimize harm. As these shifts unfold, the priority remains equitable access, privacy protections, and transparent governance to ensure that everyone can participate in the benefits of personalized medicine.
Genetics and Personalized Medicine: Breakthroughs Driving Everyday Care
Genetics breakthroughs are moving from the laboratory to the clinic, reshaping how we prevent and treat disease. With rapid advances in sequencing, tumor genomics, and pharmacogenomics, clinicians can translate complex genetic data into practical decisions that affect prevention, diagnosis, and therapy at the bedside. This shift toward precision medicine reflects ongoing genomic research and a broader effort to tailor care to individual biology, lifestyle, and values.
Health tech innovations are powering the translation of genetic insights into everyday practice by linking genetic profiles with electronic health records, real-world evidence, and decision-support tools. Patients benefit when testing informs personalized screening strategies, safer drug choices, and therapies matched to their biology, helping reduce unnecessary tests, adverse effects, and misaligned care.
Genomic Research and Precision Medicine: From Bench to Bedside
Genomic research is expanding at scale, with millions of variants mapped and linked to disease risk, progression, and treatment response. The falling costs of sequencing are making whole-genome and exome analyses feasible for broader populations, accelerating the move toward precision medicine as a standard of care.
As data science and collaboration grow, researchers and clinicians translate discovery into practice more quickly. AI-driven interpretation, interoperable data sharing, and large cancer and non-cancer cohorts feed into clinical guidelines, enabling diagnostics, risk assessment, and therapeutic decisions to be tailored to individual patients.
Pharmacogenomics in Practice: Tailoring Drugs to DNA
Pharmacogenomics sits at the core of personalized medicine advances by explaining why people respond differently to the same drug. By testing genetic variants that influence drug metabolism and receptor activity, clinicians can choose medications and doses that maximize benefit while minimizing harm.
Real-world implementation is expanding beyond rare conditions to common treatments in cardiovascular, metabolic, and mental health care. This approach reduces adverse effects, shortens the time to effective therapy, and aligns pharmacotherapy with a patient’s unique pharmacogenomic profile.
Cancer Genomics and Targeted Therapies: Personalizing Oncology
Cancer genomics and precision oncology have yielded actionable mutations that guide targeted therapies. Tumor profiling helps oncologists select drugs more likely to work and avoid ineffective regimens, potentially improving response rates and reducing collateral damage compared with traditional therapies.
Large cancer cohorts and cross-institutional data sharing are driving better predictive models and new therapeutic targets. These genetics breakthroughs illustrate how genomic research informs better care and how health tech innovations enable rapid translation into clinical practice.
Health Tech Innovations: Translating Genetic Insights into Care
Health tech innovations are the backbone of translating genetic insights into routine care. Interoperable systems, lab-to-clinic data flow, and clinician decision-support turn dense genetic findings into clear, actionable steps that fit into everyday workflows.
Integrating genetics into electronic health records and patient dashboards supports timely decisions while protecting privacy. Real-world evidence and patient-reported outcomes further refine how genetic data informs screening, prevention, and treatment choices.
Ethics, Equity, and Access in the Genomics Era
Ethical considerations, privacy, and equity are central as genetics reshapes care. Ensuring informed consent for data use, guarding against secondary findings, and preventing disparities in access are essential foundations of responsible precision medicine.
Policy, funding, and community engagement must accompany scientific advances to ensure diverse populations benefit from genetics breakthroughs and genomic research. By prioritizing equitable access and robust privacy protections, the health care system can translate genomic research into tangible improvements for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current meaning of Genetics and Personalized Medicine in healthcare, and why do genetics breakthroughs matter for patients?
Genetics and Personalized Medicine describe a shift from one-size-fits-all care to treatments tailored to a person’s genetic makeup, health history, and preferences. Genetics breakthroughs—such as improved sequencing, pharmacogenomics, and tumor profiling—are translating into faster diagnoses, more effective therapies, and fewer side effects, guiding decisions at the bedside.
How do genetics breakthroughs and genomic research enable precision medicine and personalized care?
Genomic research maps variants linked to disease risk and treatment response. With breakthroughs in sequencing cost reductions and advanced data interpretation, clinicians can estimate risk, tailor preventive strategies, and select therapies aligned with a patient’s biology, aligning with precision medicine goals.
What is pharmacogenomics and how does it illustrate personalized medicine advances in drug therapy?
Pharmacogenomics studies how genes affect drug metabolism and response. This empowers personalized medicine advances by guiding drug choice and dosing to maximize benefit and minimize adverse effects, especially for medicines with narrow therapeutic windows.
How does genomic research support precision medicine and targeted therapies in cancer and beyond?
Genomic research identifies actionable mutations and informs precision medicine in cancer; tumor profiling matches patients to targeted therapies with better outcomes and fewer collateral effects than traditional chemotherapy.
What are health tech innovations driving the integration of genetic data into electronic health records and real-world evidence for personalized medicine?
Health tech innovations include interoperable data standards, AI-powered interpretation, decision-support tools, and real-world data integration that bring genetic results into electronic health records to guide care and strengthen evidence for personalized medicine.
What should patients know about access, privacy, and ethics as genetics and personalized medicine expand?
Access, privacy protections, and informed consent are essential as genetic testing and data sharing expand. Patients should understand who can access results, potential implications for family members, and how data may be used in research to advance personalized medicine.
| Theme | What it Means | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| What’s driving the shift | Move from one-size-fits-all to precision care using genetic data, health history, and lifestyle; trends include sequencing, affordable testing, and integration of genetic data with electronic health records and real-world evidence. | Better prevention, diagnosis, and treatment; targeted and proactive care. |
| Key breakthroughs | Genomic sequencing advances reduce time and cost; pharmacogenomics in routine care; cancer genomics guiding targeted therapies; prenatal and neonatal screening. | More precise risk assessment, personalized treatment, earlier detection. |
| Patient perspective | Better diagnoses and more tolerable therapies; targeted cancer therapies; pharmacogenomics for drug choice and dosing. | Right treatment for the right patient, fewer side effects, quicker decisions. |
| Clinical and system implications | Need interoperable data, decision-support tools, privacy protections, and standardized testing pipelines; emphasize equitable access and data sharing. | Efficient workflows, consistent care, privacy and equity safeguards. |
| Road ahead | Integration of multi-omics; real-world data from diverse populations; ongoing trials and regulatory frameworks to refine tests and therapies. | More comprehensive, inclusive, evidence-based precision medicine. |
| Ethical and policy considerations | Informed consent, secondary findings, and potential family impact; policies to promote equitable access and prevent disparities. | Responsible use, privacy protection, and ensuring equitable access. |
Summary
Genetics and Personalized Medicine are at a transformative moment in health care. The convergence of faster sequencing, smarter data interpretation, targeted therapies, and patient-centered decision-making is fundamentally changing how we diagnose, treat, and prevent disease. While challenges remain—cost, access, privacy, and equity—the momentum is undeniable. By focusing on patient needs, maintaining rigorous privacy standards, and investing in interoperable systems and ongoing education, the health care community can ensure that the promise of genetics today becomes the standard of care tomorrow. As this field continues to evolve, staying informed about genetics breakthroughs, genomic research, pharmacogenomics, and precision medicine will help patients and providers make smarter, safer, and more personalized health choices.